成果发表于2022年6月15日《科学·机器人》,被AAAS News作为Highlight研究成果报道。
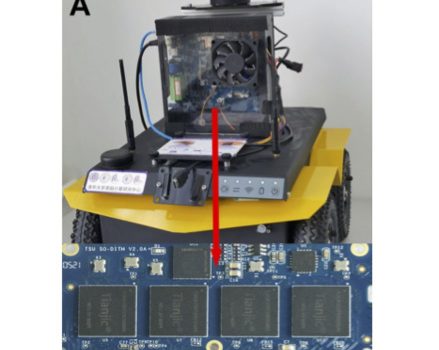
这一研究由清华大学精密仪器系教授、类脑计算研究中心主任施路平率队,研发了一款名为TianjicX的28nm神经拟态芯片。TianjicX的峰值动态能效为3.2TOPS/W,片上存储带宽为5.12tb/s,单位面积算力高达0.2TOPS/mm2,支持对每个任务进行计算资源的自适应分配和执行时间的调度。研究团队打造了一个搭载该芯片的多智能任务移动机器人Tianjicat(天机猫),并设计让它作为猫这个角色,来参与猫捉老鼠的游戏。实验结果显示,与NVIDIA Jetson TX2相比,在TianjicX上跑多个网络的延迟大幅减少了约98.74%,动态功率降低了50.66%。论文作者认为,TianjicX为移动智能机器人计算硬件的研发开辟了一条新的道路,使其能在低延迟、低功耗的情况下本地执行密集和复杂的任务,并支持多个跨计算范式神经网络模型以各种协调方式在机器人中并行执行。
神经拟态架构不仅可以用于提高智能水平,还可以为替代计算架构设计方法提供思路,包括以分散分布的方式进行资源配置、采用事件驱动的执行和调度、通过类神经网络活动实现近似计算、采用专门的硬件架构实现通用系统等等。基于这些思想,这篇论文的作者设计了Rivulet执行模型和TianjicX芯片的实现,并在设计TianjicX时,就任务执行、资源分配和任务协作方面进行了多种权衡,以实现较高的时空弹性。相较传统的神经拟态芯片,TianjicX能充分利用智能算法的数据局域性,提高内存利用率,支持多种数据移动模式,增强可编程性。
Neuromorphic computing chip with spatiotemporal elasticity for multi-intelligent-tasking robots
作者信息:Songchen Ma, Jing Pei, Wenhao Zhang, Dahu Feng, Fangwen Yu, Chenhang Song, Huanyu Qu, Cheng Ma, Mingsheng Lu, Faqiang Liu, Wenhao Zhou, Yujie Wu, Yihao lin, Hongyi Li, Taoyi Wang, Jiuru Song, Xue Liu, Guoqi Li, Rong Zhao, Luping Shi*
DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.abk2948
Recent advances in artificial intelligence have enhanced the abilities of mobile robots in dealing with complex and dynamic scenarios. However, to enable computationally intensive algorithms to be executed locally in multitask robots with low latency and high efficiency, innovations in computing hardware are required. Here, we report TianjicX, a neuromorphic computing hardware that can support true concurrent execution of multiple cross-computing-paradigm neural network (NN) models with various coordination manners for robotics. With spatiotemporal elasticity, TianjicX can support adaptive allocation of computing resources and scheduling of execution time for each task. Key to this approach is a high-level model, “Rivulet,” which bridges the gap between robotic-level requirements and hardware implementations. It abstracts the execution of NN tasks through distribution of static data and streaming of dynamic data to form the basic activity context, adopts time and space slices to achieve elastic resource allocation for each activity, and performs configurable hybrid synchronous-asynchronous grouping. Thereby, Rivulet is capable of supporting independent and interactive execution. Building on Rivulet with hardware design for realizing spatiotemporal elasticity, a 28-nanometer TianjicX neuromorphic chip with event-driven, high parallelism, low latency, and low power was developed. Using a single TianjicX chip and a specially developed compiler stack, we built a multi-intelligent-tasking mobile robot, Tianjicat, to perform a cat-and-mouse game. Multiple tasks, including sound recognition and tracking, object recognition, obstacle avoidance, and decision-making, can be concurrently executed. Compared with NVIDIA Jetson TX2, latency is substantially reduced by 79.09 times, and dynamic power is reduced by 50.66%.